Tiny White Bumps on a Baby's Nose and Cheeks
Many things can cause a rash in babies and children, and they're often nothing to worry about.
As a parent, you may know if your child seems seriously unwell and should trust your own judgement.
Rash with a high temperature
Rash on cheeks with high temperature
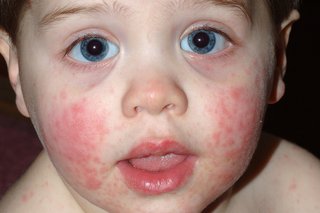
A rash on 1 or both cheeks plus a high temperature, runny nose, sore throat and headache may be slapped cheek syndrome. After a few days, a rash may appear on their body.
Slapped cheek syndrome usually gets better on its own within 3 weeks. Children's paracetamol or ibuprofen can bring down a high temperature.
Blisters on hands and feet plus mouth ulcers
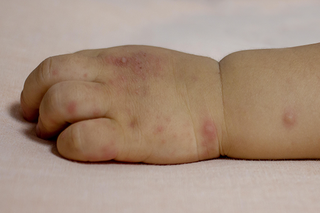
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a common childhood illness that causes blisters on the hands and feet, and ulcers in the mouth. It also causes a high temperature and your child may have a sore throat.
It usually gets better in 7 to 10 days. Children's paracetamol can bring down a high temperature.
Rash on the face and body
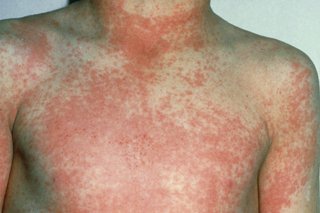
Scarlet fever causes a rash that looks like pinpricks and feels rough, like sandpaper. The rash can be red, but this may be less noticeable on brown and black skin.
Scarlet fever usually starts with a white coating on the tongue, a sore throat, headache and a high temperature.
See a GP immediately if you think your child has scarlet fever. It's treated with antibiotics.
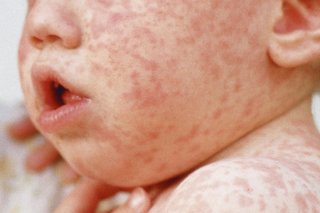
Measles usually starts with the same symptoms as a cold, plus a high temperature, sore eyes that are sensitive to light and grey spots inside the cheeks.
After a few days, a spotty rash appears on the head or neck and spreads to the rest of the body. The spots can appear red or brown, but they may be less noticeable on brown and black skin.
Call a GP if you think your child has measles.
Rash with itching
Rash caused by heat
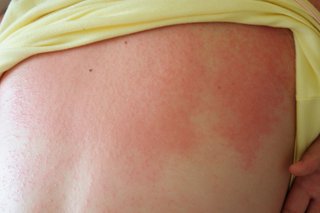
Heat and sweat can cause raised spots or patches known as prickly heat or heat rash. The rash can look red, but it may be less noticeable on brown or black skin.
It itches, so you may notice your child scratching.
Heat rash usually gets better on its own after a few days.
Scaly or cracked skin
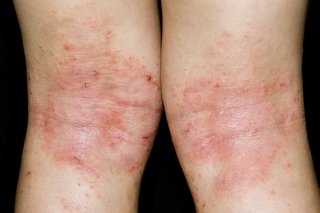
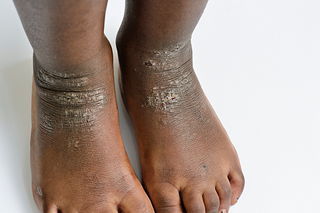
Skin that's itchy, dry and cracked may be atopic eczema. It's common behind the knees, elbows and neck, but it can appear anywhere.
The affected area may change colour. On white skin, the area may look pink or red. On brown and black skin, it may look grey or purple, or darker than surrounding skin.
Speak to a GP if you think your child has eczema.
Raised, itchy spots or patches
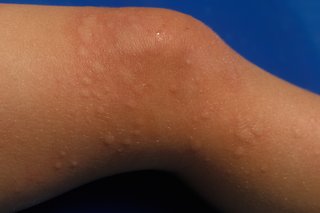
Hives causes a raised, itchy rash. It can look red, but this may be less noticeable on brown and black skin.
The rash can be a sign of an allergic reaction to things like a sting, medicine or food.
It usually gets better within a few days.
Speak to a GP if your child keeps getting this type of rash. They may be allergic to something.
Call 999 if there's swelling around their mouth.
Itchy round rash
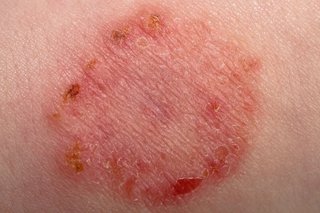
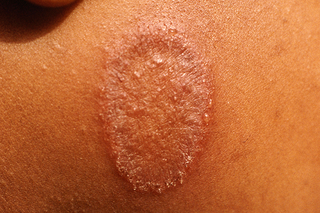
An itchy, dry, ring-shaped patch of skin may be ringworm. The patch may look red, pink, silver, or darker than surrounding skin.
Ask a pharmacist for a cream or lotion to treat ringworm.
Speak to a GP if it appears on your child's scalp, as it may need to be treated with prescription medicine.
Small spots and blisters
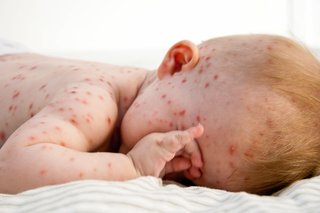
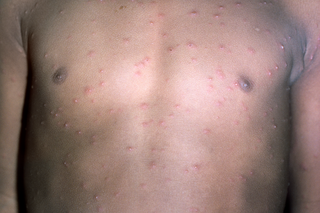
Chickenpox starts with small, itchy spots. The spots may look red, pink, the same colour or darker than surrounding skin, depending on your child's skin tone. At the start, the spots may be harder to see on brown and black skin.
The spots quickly form blisters and then scabs.
Some children have a few spots, while others have them all over their body.
Itchy sores or blisters
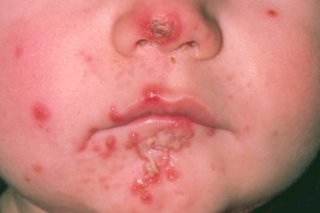
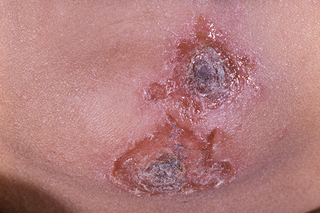
Red sores or blisters that burst and leave crusty, golden-brown patches could be impetigo. The redness may be harder to see on brown and black skin.
The sores or blisters can be itchy, get bigger or spread to other parts of the body. They often appear on the face, hands or around the middle of the body.
Speak to a GP if you think your child may have impetigo.
Tiny and very itchy spots
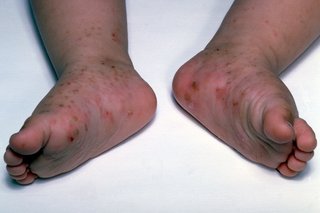
Scabies is caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin.
Ask a pharmacist for a cream or lotion to treat scabies. Everyone in the household needs to be treated at the same time – even if they do not have symptoms.
You should take your baby to a GP for advice if they are under 2 months old.
Rash without fever or itching
Tiny spots on a baby's face

Very small spots, called milia, often appear on a baby's face when they're a few days old.
Milia may appear white or yellow, depending on your baby's skin tone.
They usually go away within a few weeks and do not need treatment.
Red, yellow and white spots in babies
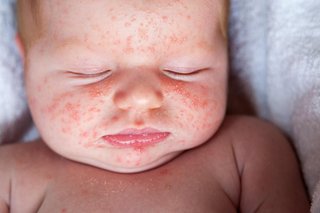
Raised red, yellow and white spots (erythema toxicum) can appear on babies when they're born. They usually appear on the face, body, upper arms and thighs.
The rash can disappear and reappear.
It should get better in a few weeks without treatment.
Pink or skin-coloured spots
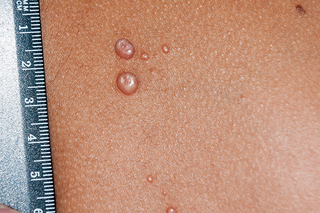
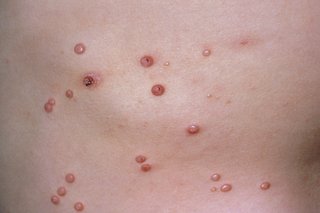
Small, firm, raised spots that can appear anywhere on the body are common in children and known as molluscum contagiosum.
The spots can be the same colour as surrounding skin, darker than surrounding skin, or pink.
Treatment is not recommended because the spots get better on their own, although it can take more than a year.
Red patches on a baby's bottom
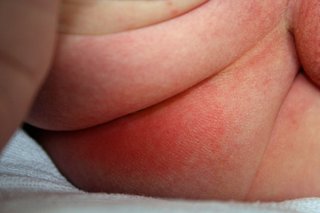
With nappy rash your baby's skin may look sore and feel hot. There may be red patches on your baby's bottom or around the whole nappy area.
There may be spots or blisters. It can make your child feel uncomfortable or distressed.
You can buy cream from a pharmacy to help.
Pimples on the cheeks, nose and forehead
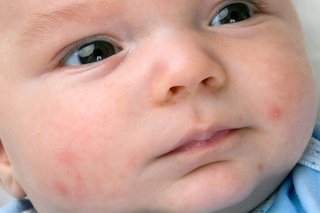
Baby acne can appear within a month after birth but usually gets better after a few weeks or months.
Washing your baby's face with water and a mild moisturiser can help.
Do not use acne medicines intended for older children and adults.
Yellow, scaly patches on the scalp
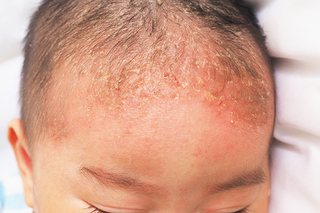
Cradle cap is when a baby gets yellow or white, greasy, scaly patches on their scalp.
It usually gets better without treatment in a few weeks or months.
Gently washing your baby's hair and scalp with baby shampoo may help prevent more patches.
Page last reviewed: 11 June 2021
Next review due: 11 June 2024
Tiny White Bumps on a Baby's Nose and Cheeks
Source: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/rashes-babies-and-children/
0 Response to "Tiny White Bumps on a Baby's Nose and Cheeks"
Post a Comment